How to use NetShark LLDP Decode Feature introduced in 10.9 release ?
NetShark : How to use NetShark LLDP Decode Feature ?

Issue

Solution
NetShark release 10.9 supports the LLDP Decoding. The Link Layer Discovery Protocol (LLDP) is a vendor-neutral Layer 2 protocol in the Internet Protocol Suite used by network devices to advertise their identity, capabilities, and neighbors on an IEEE 802 local area network, principally wired Ethernet.
An LLDP agent transmits information about the capabilities and current status of the system associated with its MAC Service access point identifier. Transmission can be initiated either by the expiration of a transmit countdown timing counter or by a change in the value of one or more of the information elements (managed objects) associated with the local system. When a transmit cycle is initiated, the LLDP management entity extracts the managed objects from the LLDP local system MIB and formats this information into TLVs. The TLVs are inserted into an LLDPDU that is passed to the LLDP transmit module.
Starting with NetShark version 10.9 NetShark can decode LLDP traffic and provide information on network devices and their capabilities. A new view, LLDP Port Configuration, has been added to Packet Analyzer (LAN and Network > LLDP). This view can be used with live or captured traffic sources.
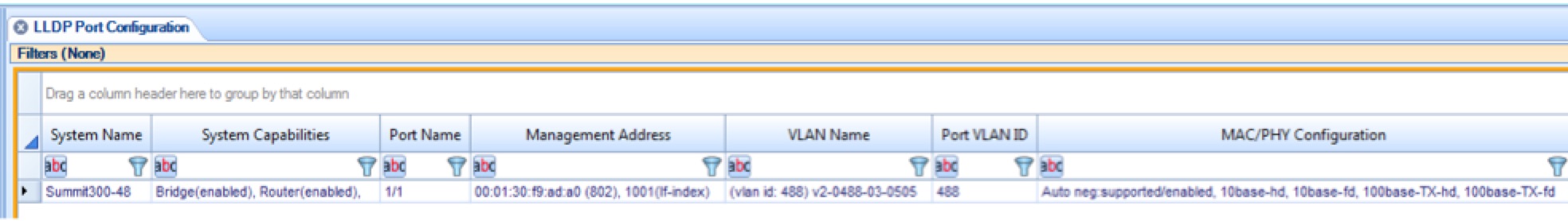
This view summarizes the capabilities and status transmitted by LLDP agents on network devices. Use the View Editor to add additional fields or customize the view for your specific network device information requirements.
The Ethertype of an LLDP Ethernet frame is 0x88CC. Ethernet frames of this Ethertype are processed to extract a sequence of variable length information elements (TLVs) contained in the Link Layer Discovery Protocol Data Unit (LLDPDU).
The following LLDP fields are extracted from an LLDPDU and are available for use in views:
|
Field Name |
Field Description |
Format |
|
lldp.port_id |
Port name of LLDP interface |
MAC address, network address, local backplane or something else, depending on the value of the port ID subtype. |
|
lldp.port_desc |
Port description |
IEEE 802 LAN station’s port description. |
|
lldp.sys_name |
System name for DNS lookup |
Alpha-numeric string indicating the system’s administratively assigned name. |
|
lldp.sys_desc |
System make, model, version |
Should include the full name and version identification of the system’s hardware type, software operating system, and networking software. |
|
lldp.capabilities |
Primary system capabilities and status |
<cap 1 name>(enabled/disabled), … <cap ‘n’ name>(enabled/disabled) |
|
lldp.mgmt_addr |
Management address Identifies an address associated with the local LLDP agent that may be used to reach higher layer entities to assist discovery by network management. |
<mgmt-address formatted as per addr family> (IP/802), <number>(if-index/port-num), <oid string>(OID) Note: Since there are typically a number of different addresses associated with a MAC Service Access Point identifier, an individual LLDPDU may contain more than one Management Address TLV. |
|
lldp.vlan_name |
VLAN ID and name |
vlan id: <number> <vlan name string> |
|
lldp.port_vlan_id |
VLAN ID assigned to this port |
VLAN identifier (PVID) that is associated with untagged or priority tagged frames (IEEE 802.1Q- 2005). |
|
lldp.port_proto_vlan_id |
Used by a bridge port to advertise a port and protocol VLAN ID. |
0 – 4094 |
|
lldp.mac_phy |
Physical layer and duplex configuration of sending IEEE 802.3 LAN node |
Auto neg: (supported/enabled/disabled/not-supported; PMD Mode: ) <comma separated list of physical layer configurations> |
If a given LLDPDU does not have a TLV for a field, the default value “N/A” is used. Rows are listed by the time of their last update. The most recently updated rows appear at the top of the grid.
Note: Duplicate rows are aggregated, that is, the view shows only the latest information received from each LLDP sender.
Troubleshooting
If LLDP traffic is not processed properly, please open a TAC case and provide a capture file with a few packets.

Environment
NetShark

Related Bugs

Attachments

